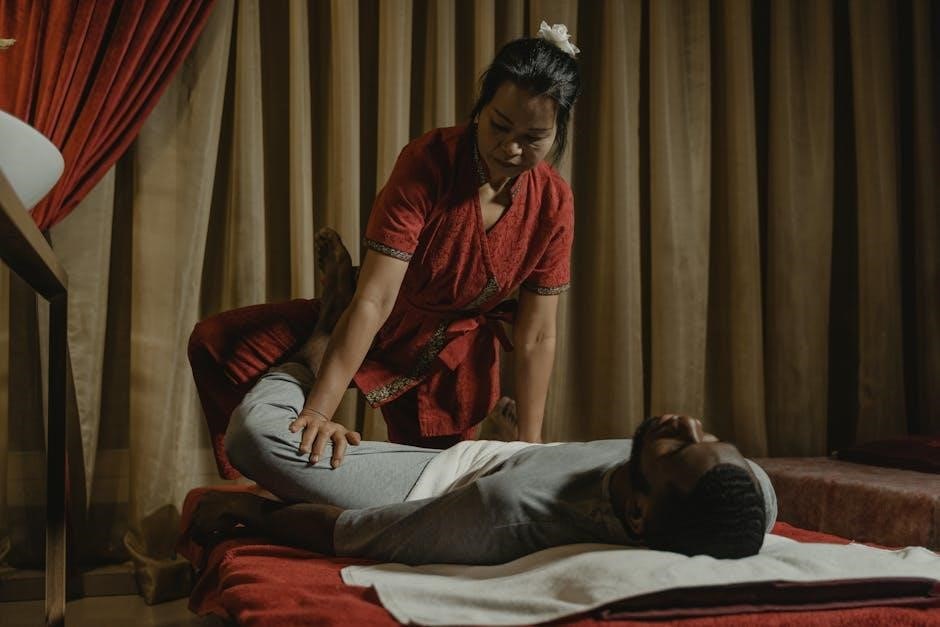
Sacroiliac (SI) joint pain often stems from dysfunction in the joint connecting the pelvis and lower back. Gentle stretches and exercises can alleviate discomfort and improve mobility. This article explores effective techniques and professional guidance for managing SI joint pain through stretching and strengthening exercises.
1.1 Overview of SI Joint Pain
Sacroiliac (SI) joint pain is a common condition affecting the joint that connects the sacrum and ilium bones in the pelvis. This joint plays a crucial role in absorbing shock and facilitating movement between the spine and legs. Pain in the SI joint often manifests as discomfort in the lower back, buttocks, or thighs, and it can range from mild to debilitating. The pain may be acute or chronic, stemming from inflammation, dysfunction, or instability in the joint. Activities such as running, twisting, or prolonged sitting can exacerbate symptoms. While rest and ice can provide temporary relief, targeted stretches and exercises are essential for long-term management. Understanding the root cause of SI joint pain is key to developing an effective treatment plan. This overview highlights the importance of addressing the joint’s unique role in mobility and stability to alleviate discomfort and restore function.
1.2 The Role of Stretches in Relieving SI Joint Pain
Stretches play a vital role in alleviating sacroiliac joint pain by improving flexibility, reducing stiffness, and enhancing joint mobility. Gentle stretching exercises can help relax tight muscles around the SI joint, such as the piriformis and hamstrings, which often contribute to pain and discomfort. Regular stretching can also improve posture and reduce inflammation, creating a more stable environment for the joint. Additionally, stretches can strengthen the surrounding muscles, providing better support to the SI joint and preventing future flare-ups. It’s important to perform these stretches slowly and within a pain-free range to avoid aggravating the condition. Consistency is key, as regular practice yields the best results in managing SI joint pain effectively. Over time, a well-designed stretching routine can significantly enhance comfort and overall quality of life for individuals suffering from SI joint dysfunction.
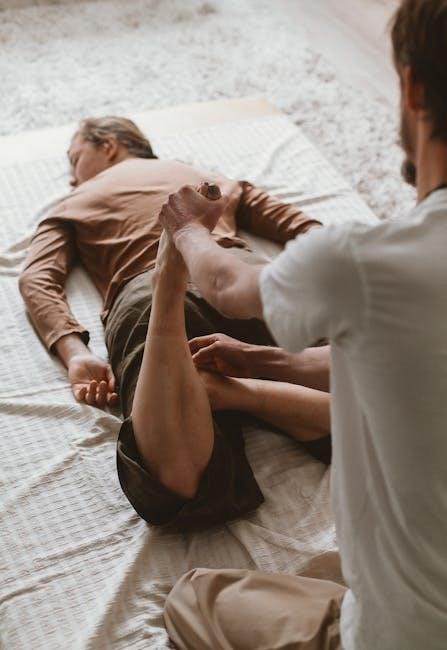

Understanding the Sacroiliac (SI) Joint
The sacroiliac (SI) joint connects the sacrum and ilium, playing a crucial role in supporting the spine and pelvis while enabling essential movements like walking.
2.1 Anatomy and Function of the SI Joint
The sacroiliac (SI) joint is a synovial joint connecting the sacrum (base of the spine) and the ilium (part of the pelvis). It is supported by strong ligaments and cartilage, allowing limited movement while providing stability. The SI joint plays a crucial role in absorbing shock and distributing weight during activities like walking or twisting. Its primary function is to connect the spine and pelvis, enabling mobility while maintaining structural integrity. While the SI joint is generally stable, inflammation or dysfunction can lead to pain, often felt in the lower back or buttocks. Understanding its anatomy is essential for addressing pain and developing effective treatment strategies.
2.2 Common Causes of SI Joint Pain
Sacroiliac (SI) joint pain often arises from inflammation, trauma, or dysfunction. Common causes include pregnancy, which relaxes the joint, and activities like running or twisting, which can strain it. Injuries, such as falls or car accidents, may also trigger pain. Additionally, conditions like arthritis or uneven leg lengths can contribute to SI joint dysfunction. Pain typically occurs in the lower back or buttocks and may radiate to the thighs. Understanding these causes is key to addressing symptoms effectively.
Best Stretches for SI Joint Pain Relief
Effective stretches for SI joint pain relief include knee-to-chest, piriformis, and cat-cow stretches. These exercises target tight muscles and improve joint mobility, reducing discomfort and enhancing flexibility.
3.1 Knee-to-Chest Stretch
The knee-to-chest stretch is an effective exercise for alleviating SI joint pain. To perform this stretch, lie on your back with knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Gently bring one knee toward your chest, holding onto your knee with your hands. Ensure the movement is smooth and pain-free, avoiding any sharp discomfort. Hold the stretch for 20-30 seconds before slowly releasing. Repeat on the other side to maintain balance. This stretch helps to relax the muscles around the SI joint, improving flexibility and reducing stiffness. It is essential to perform this exercise gently to avoid exacerbating the pain. Regular practice can contribute to overall lower back relief and improved joint mobility.
3.2 Piriformis Muscle Stretch
The piriformis muscle stretch is a highly effective exercise for relieving SI joint pain, as tightness in this muscle can directly impact joint mobility. To perform this stretch, lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Cross the ankle of the affected side over the opposite knee, forming a figure-4 position. Gently pull the unaffected knee toward your chest until a mild stretch is felt in the buttock area. Hold this position for 20-30 seconds, breathing deeply to relax the muscle. Avoid any sharp pain; the stretch should feel comfortable. Repeat on the other side if needed. This exercise helps to release tension in the piriformis muscle, which often contributes to SI joint dysfunction and lower back discomfort. Regular practice can enhance flexibility and reduce pain.
3.3 Cat-Cow Stretch
The Cat-Cow Stretch is a gentle, flowing exercise that promotes spinal flexibility and relieves tension in the lower back, which can indirectly benefit the SI joint. Start on your hands and knees in a tabletop position, keeping your spine neutral. Inhale as you arch your back, lifting your head and tailbone toward the ceiling (Cow Pose). Then, exhale as you round your spine, tucking your chin and pelvis toward the floor (Cat Pose). Repeat this sequence 10-15 times, moving slowly and smoothly. This stretch improves mobility and reduces stiffness, making it an excellent addition to an SI joint pain relief routine. It’s low-impact and can be modified to suit different fitness levels, providing a soothing and effective way to maintain spinal health.
3.4 Child’s Pose Stretch
Child’s Pose (Balasana) is a restorative stretch that targets the lower back and hips, providing relief for SI joint pain. To perform this stretch, kneel on the floor with your knees wide apart and toes touching. Sit back onto your heels and stretch your arms forward, lowering your chest toward the ground. Keep your forehead on the mat and relax your body. Hold this pose for 20-30 seconds, breathing deeply. This stretch gently elongates the spine and pelvic muscles, reducing tension around the SI joint. It is particularly beneficial for those experiencing stiffness or discomfort in the lower back and sacral area. Regular practice of Child’s Pose can enhance flexibility and promote relaxation, making it an excellent addition to an SI joint pain relief routine. Always ensure proper form to avoid strain and maximize benefits.
3.5 Hamstring Stretch on the Wall
The Hamstring Stretch on the Wall is an effective stretch for relieving SI joint pain by targeting tight hamstrings, which often contribute to discomfort in the lower back and pelvis. To perform this stretch, lie on your back with your buttocks close to a wall. Place one leg straight up against the wall, keeping your knee straight, while the other leg remains bent on the floor for stability. Hold the stretch for 20-30 seconds and then switch legs. This stretch helps lengthen the hamstrings, reducing tension that can strain the SI joint. It also improves pelvic alignment and promotes relaxation in the lower back muscles. Regular practice of this stretch can enhance flexibility and reduce stiffness, making it a valuable addition to an SI joint pain relief routine.

Exercises to Strengthen the SI Joint
Strengthening exercises for the SI joint focus on improving stability and muscle support around the pelvis and lower back. These exercises, such as bridging and pelvic tilts, help stabilize the joint, reduce pain, and enhance mobility by strengthening the surrounding muscles.
4.1 Bridging Exercise
The bridging exercise is an effective strengthening technique for the SI joint. To perform this exercise, lie on your back with knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Engage your core muscles by drawing your belly button towards your spine. Slowly lift your hips towards the ceiling while keeping your shoulders on the ground, forming a straight line from knees to chest. Hold this position for 5-10 seconds before slowly lowering your hips back down. This movement strengthens the glutes, hamstrings, and lower back muscles, which are crucial for SI joint stability. It is important to maintain proper form to avoid strain. Perform 3 sets of 10-15 repetitions for optimal results.
4.2 Pelvic Tilt Exercise
The pelvic tilt exercise is a gentle and effective way to improve flexibility and stability in the SI joint. To perform this exercise, lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Engage your core muscles by drawing your belly button toward your spine. Gently tilt your pelvis upward, flattening your lower back against the floor, and hold for 5 seconds. Repeat this motion 10-15 times, ensuring smooth, controlled movements. This exercise strengthens the abdominal and pelvic muscles, which helps stabilize the SI joint and reduce pain. Avoid arching your back or using jerky movements, as this could exacerbate discomfort; Perform 2-3 sets daily for optimal benefits.
4.3 Clamshell Exercise
The clamshell exercise targets the glutes and improves sacroiliac joint stability. Lie on your side with knees bent and feet touching. Slowly lift the top knee toward the ceiling without moving your feet or hips. Hold for 5 seconds, then lower. Perform 2-3 sets of 10-15 repetitions on each side. This exercise strengthens the gluteus medius muscle, which supports SI joint function. Keep your core engaged to maintain proper form and avoid arching your back. If pain occurs, modify by reducing the range of motion. Consistency in this exercise can enhance joint stability and reduce discomfort. It’s a low-impact activity suitable for most individuals with SI joint pain, promoting strength and flexibility in the pelvic region.

Physical Therapy for SI Joint Pain
Physical therapy is a key component in managing SI joint pain, offering personalized exercises and expert guidance to restore joint mobility and strength while addressing underlying issues.
5.1 Role of a Physiotherapist in SI Joint Rehabilitation
A physiotherapist plays a pivotal role in SI joint rehabilitation by designing tailored exercise programs, providing manual therapy, and educating patients on proper posture and movement techniques. They assess each patient’s specific condition to identify the root cause of pain, ensuring exercises are both safe and effective. Through hands-on treatments like joint mobilization and soft tissue work, physiotherapists help restore joint mobility and reduce stiffness. Additionally, they teach patients how to perform stretches and strengthen surrounding muscles to enhance stability and prevent future flare-ups. Regular follow-ups allow for progress monitoring and adjustments to the treatment plan, ensuring a comprehensive approach to recovery. Their expertise supports patients in achieving long-term relief and improved functional abilities.
5.2 Recommended Exercises by Physical Therapists
Physical therapists often recommend exercises that target the SI joint and surrounding muscles to improve stability and reduce pain. Bridging exercises are commonly suggested to strengthen the glutes and pelvic muscles. Pelvic tilts are another effective option, focusing on core engagement and gentle spinal movement. Clamshell exercises, performed by squeezing the knees together while lying on one side, help strengthen the hip and pelvic muscles. These exercises are designed to enhance joint stability, improve posture, and reduce strain on the SI joint. Therapists may also incorporate gentle stretching, such as the knee-to-chest stretch, to relieve tension in the lower back and pelvis. Consistency in performing these exercises is key to achieving long-term relief and preventing future discomfort.

Lifestyle Modifications to Prevent SI Joint Pain
Maintaining proper posture, avoiding aggravating activities, and using supportive gear can help prevent SI joint pain. These modifications promote joint stability and reduce strain on the sacroiliac joint.
6.1 Maintaining Proper Posture
Maintaining proper posture is crucial for preventing SI joint pain. When sitting or standing, ensure your spine is aligned, with shoulders back and pelvis in a neutral position. Avoid slouching or leaning forward, as this can strain the SI joint. Use ergonomic chairs and consider a supportive cushion to promote proper spinal alignment. During activities, be mindful of your posture to reduce unnecessary stress on the SI joint. This simple yet effective practice can significantly contribute to long-term joint health and pain prevention.
6.2 Avoiding Activities That Exacerbate Pain
Identifying and avoiding activities that worsen SI joint pain is essential for managing symptoms. High-impact exercises, such as running or repetitive twisting, can strain the joint and increase discomfort. Heavy lifting or bending should also be minimized to prevent further irritation. Activities that involve uneven surfaces or prolonged sitting in an unsupported position may exacerbate pain. It’s important to assess your daily routine and modify movements that trigger discomfort. Gradually reintroducing activities after rest and incorporating stabilizing exercises can help improve joint resilience. Consulting a healthcare professional to tailor activity modifications to your specific condition ensures a safer and more effective approach to pain management.
6.3 Using Supportive Gear for SI Joint Stability
Using supportive gear can significantly enhance SI joint stability and reduce pain. An SI joint belt or brace provides compression and alignment support, especially during physical activity. Orthotics or shoe inserts can address uneven gait patterns that strain the joint. Compression shorts or supportive underwear may also help maintain proper pelvic alignment. These tools are particularly beneficial for individuals with SI joint dysfunction or those recovering from injury. However, they should be used in conjunction with exercises and stretches rather than as a standalone solution. Consulting a healthcare professional ensures proper fitting and selection of gear tailored to individual needs. Regular use of supportive devices can promote joint stability and prevent exacerbation of pain during daily activities or exercise.
When to Seek Professional Help
Seek professional help if SI joint pain persists, worsens, or radiates to other areas. Consult a healthcare professional if pain exceeds 4/10, or if self-care measures fail to relieve symptoms.
7.1 Red Flags: When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
Certain symptoms indicate the need for immediate professional consultation. Severe pain exceeding 4/10, radiating pain down the legs, or numbness and tingling should prompt a visit to a healthcare provider. Additionally, if pain persists despite self-care measures or worsens over time, seeking medical advice is crucial. A physiotherapist can provide personalized exercises and treatments tailored to address SI joint dysfunction effectively. Ignoring these red flags may lead to prolonged recovery or further complications. Professional guidance ensures proper diagnosis and treatment, preventing potential long-term issues. Consulting a specialist is essential for managing severe or persistent SI joint pain to restore mobility and alleviate discomfort.
7.2 Importance of Proper Diagnosis for SI Joint Pain
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effectively managing SI joint pain. Misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate treatments, delaying recovery. A healthcare professional will assess symptoms, medical history, and perform physical examinations to confirm SI joint dysfunction. Imaging studies, such as X-rays or MRIs, may be used to rule out other conditions like herniated discs or arthritis. Proper diagnosis ensures targeted therapies, reducing the risk of prolonged pain or complications. A delayed or incorrect diagnosis can result in ineffective treatments and prolonged discomfort. Consulting a specialist, such as a physiotherapist or orthopedist, is vital for a comprehensive evaluation. Professional guidance ensures personalized treatment plans, addressing the root cause of pain and promoting optimal recovery. Early and accurate diagnosis is key to achieving long-term relief and preventing further issues.
SI joint pain can be effectively managed with targeted stretches and exercises, promoting relief and prevention. Consistency is key, and professional guidance ensures optimal outcomes for long-term comfort.
8.1 Summary of Effective Stretches for SI Joint Pain
Effective stretches for SI joint pain include the knee-to-chest stretch, piriformis stretch, cat-cow stretch, and child’s pose. These exercises target the surrounding muscles, improving joint mobility and reducing discomfort. Gentle movements like the hamstring stretch on the wall and pelvic tilts also provide relief. Consistency is crucial, as regular practice helps maintain joint stability and prevents exacerbation of symptoms. It’s important to perform stretches within a pain-free range and gradually increase intensity. Combining these stretches with strengthening exercises, such as bridging and clamshell exercises, enhances outcomes. Consulting a physiotherapist ensures personalized routines tailored to specific needs, promoting long-term relief and functional improvement.
8.2 The Importance of Consistency in Exercise Routine
Consistency in an exercise routine is vital for managing SI joint pain effectively. Regular stretching and strengthening exercises help maintain joint stability and prevent flare-ups. Over time, consistent practice improves muscle flexibility and strength, reducing discomfort and enhancing mobility. Skipping workouts can lead to stiffness and renewed pain, emphasizing the need for a regular schedule. Even brief daily sessions can yield significant benefits, making it easier to incorporate exercises into a busy lifestyle. Patience is key, as progress may be gradual. By committing to a consistent routine, individuals can achieve long-term relief and improve their overall quality of life, ensuring the SI joint remains healthy and functional.
